
#Ssh copy rsa key install
-C "My web-server key" : Set a new comment.Ģ: Install the public key in remote server. -f ~/.ssh/ : Specifies the filename of the key file. -b 4096 : Specifies the number of bits in the key to create. The possible values are “rsa1” for protocol version 1 and “dsa”, “ecdsa”, “ed25519”, or “rsa” for protocol version 2. -t rsa : Specifies the type of key to create. $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f ~/.ssh/ -C "My web-server key" The following syntax specifies the 4096 of bits in the RSA key to creation (default 2048): $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub – contain your public key. $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa– contains your private key. You should see two new files in $HOME/.ssh/ directory: I suggest that you setup a passphrase when prompted. You will be prompted to supply a passphrase (password) for your private key. I recommend you use the default location if you do not yet have another key there, for example: $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa. You need to set the Key Pair location and name. Your identification has been saved in /Users/vivek/.ssh/id_rsa. Sample outputs: Generating public/private rsa key pair.Įnter file in which to save the key (/Users/vivek/.ssh/id_rsa):Įnter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): You must generate both a public and a private key pair. 
How do I set up public key authentication?

Test your password less ssh keys login using ssh command.
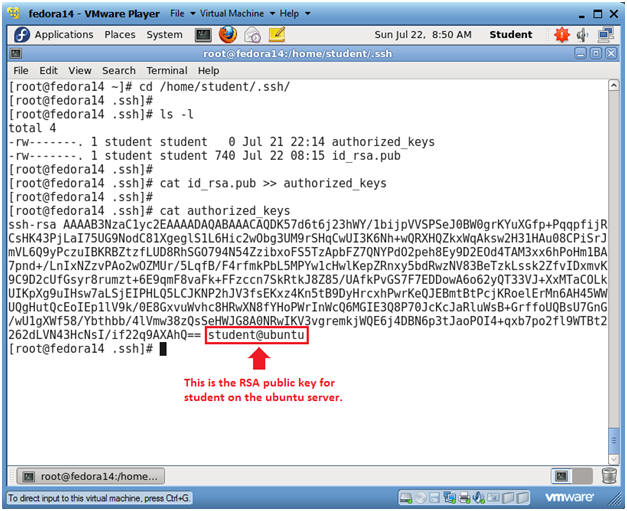
Disable the password login for root account. Add yourself to sudo or wheel group admin account. Copy and install the public ssh key using ssh-copy-id command on a Linux or Unix server. Create the ssh key pair using ssh-keygen command. This method is recommended on a VPS, cloud, dedicated or even home based server. It is an alternative security method to using passwords. OpenSSH server supports various authentication schema. OpenSSH ssh client and friends on Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, BSD, RHEL, CentOS, MacOS/OSX, AIX, HP-UX and co).










